KRAS inhibitor Cmpd2
CAS No. ——
KRAS inhibitor Cmpd2( —— )
Catalog No. M16986 CAS No. ——
KRAS inhibitor Cmpd2 is a small-molecule compound that blocks biochemical and cellular functions of KRASG12V with IC50 of 0.8 uM in vitro.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameKRAS inhibitor Cmpd2
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKRAS inhibitor Cmpd2 is a small-molecule compound that blocks biochemical and cellular functions of KRASG12V with IC50 of 0.8 uM in vitro.
-
DescriptionKRAS inhibitor Cmpd2 is a small-molecule compound that blocks biochemical and cellular functions of KRASG12V with IC50 of 0.8 uM in vitro; inhibits cell proliferation in SW1990 cells with EC50 of 2.7 uM; the potency of Cmpd2 was strongly enhanced when prenylated K-RAS4B is associated with a lipid bilayer.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMAPK/ERK Signaling
-
TargetRas
-
RecptorRas
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number——
-
Formula Weight446.773
-
Molecular FormulaC21H21BrClN3O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
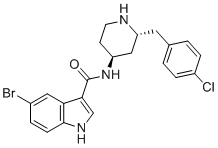
Chemical Name5-bromo-N-((2R,4S)-2-(4-chlorobenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Fang Z, et al. Cell Chem Biol. 2018 Aug 14. pii: S2451-9456(18)30261-7.
2. Jansen JM, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Apr 6;12(4):e0174706.
molnova catalog



related products
-
KRas-IN-1
A chemical fragment hit that binds to K-Ras (G12D) with affinities of 1.3-2 mM.
-
KRAS inhibitor C6ME
KRAS inhibitor C6ME is a small-molecule compound that blocks biochemical and cellular functions of KRASG12V in vitro.
-
KRAS G12C inhibitor ...
A potent, selective, covalent KRAS G12C inhibitor that selectively inhibit KRAS G12C-dependent signaling and cancer cell growth at sub-micromolar concentrations.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


